

- Duplicacy hash commandline install#
- Duplicacy hash commandline archive#
- Duplicacy hash commandline full#
- Duplicacy hash commandline download#
- Duplicacy hash commandline free#
If you want to try the reverse and actually have a go at identifying the file from a hash value, you might like to look at this article.
Duplicacy hash commandline free#
Of course, feel free to tell us about the hash program you like best. There are dozens of these tools about, and you might already have your favorite.
Duplicacy hash commandline download#
A download link is on the same page.ĭownload Microsoft File Checksum Integrity Verifier

Duplicacy hash commandline full#
It’s odd this tool has no support because it has a proper knowledge base designation of KB841290 and there is a full page on the Microsoft website detailing FCIV’s usage. It has a few more advanced options than the other two commands, including recursing into subdirectories, an exclusions list and the ability to save/list/verify checksums in an XML database.īy default, FCIV outputs MD5 checksums but you can change this to SHA1 by appending -SHA1 or -Both to output MD5 and SHA1 at the same time. The File Checksum Integrity Verifier (FCIV) is from way back in 2004 and Microsoft offers no support for it. This last tool is not built into Windows but is still made by Microsoft. Note that like the Certutil tool, only one hashing method can be entered into the command at a time. You can change this by adding -a and the new algorithm, MD5, SHA1, SHA384, SHA512, MACTripleDES, and RIPEMD160 are supported. Just supplying the file to the get-filehash command will output the hash as SHA256 by default.
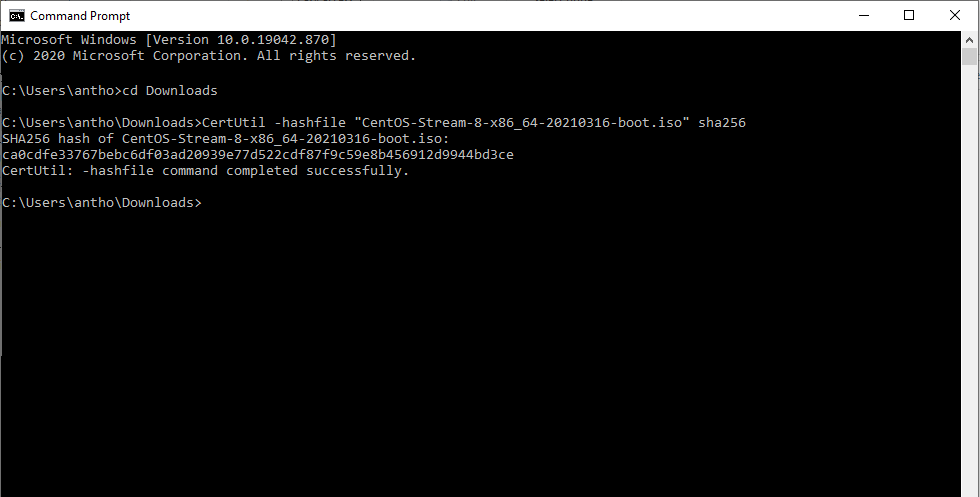
Duplicacy hash commandline install#
Windows 7 users will need to manually install PowerShell version 4 or above for this command to work. The PowerShell function is also built into Windows so needs no external executable. Only one algorithm is supported at a time, so if you want SHA1 and MD5 you will have to run the tool twice. Other algorithms are supported, just append MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA256, SHA384, or SHA512 to the line and it will show that value instead. This will output the SHA1 checksum of the file. The command to use for a file is as follows. One of its functions is being able to show the hash of a file, which is what we are looking for. They can be useful for adding into scripts or creating simple drag and drop shortcuts and etc.ĬertUtil is a command line tool that is primarily for showing information for and handling digital certificates on the system. We’ve grouped these three options together as they are all by Microsoft and the first two are built into Windows. Enabling the log file will keep a history of processed hashes and any comparison results.ĭownload Hasher (version 1.20 is at the bottom)ġ0. The current hash can be copied to the clipboard and you can manually compare the current hash value with a previous one from the clipboard or the next file that gets checked. This older version is a small executable and will give you hash values for CRC32, MD5, SHA-1, and ELF.
They do have more available hashes and folder/multi-file support if you feel like trying one out. We are looking at version 1.20 from 2009 as all the later versions have a five second nag window on startup, so we really can’t recommend them. Not to be confused with the Igorware tool at the top of our list, this hashing tool is pretty simple to use and lets you drag and drop or browse for a single file to get a checksum. You can compare the current file with a hash value in the clipboard by using the Hash Comparison box or use the “Compare a file” button to compare another file with the selected one. These include the Keccak, RIPEMD, SHA and MD families along with several others like GOST, ED2K, Adler32, and Tiger. Pressing Settings gives access to an impressive selection of 27 additional hash values that can all be displayed. One major limitation HashTab has compared to HashCheck is it only works on one file at a time.

After right clicking on the file and going to Properties, the tab is called “File Hashes” and you will get CRC32, MD5 and SHA-1 hash values displayed by default. HashTab is another tool that uses the system file properties window to show file hashes and is quite similar to HashCheck. The 7z.exe command line tool has this function by using the “h” command along with a hash switch “-scrc. Do note that when you select multiple files 7-Zip will give the overall checksums for all files added together and not each file individually. Just right click on a file and go to “CRC SHA” and the options will be available to get a checksum for CRC-32, CRC-64, SHA1, SHA256, or the asterisk will get all at once (including BLAKE2sp). A few years later a function was added to 7-Zip that introduced a context menu entry where you can quickly check a file’s integrity through the program’s user interface. The ability to verify file checksums with CRC or SHA has been in 7-Zip since 2011.
Duplicacy hash commandline archive#
Not least because of its 7z archive format that can achieve great compression ratios. 7-Zip is probably the most popular and well known free file archiver around today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
